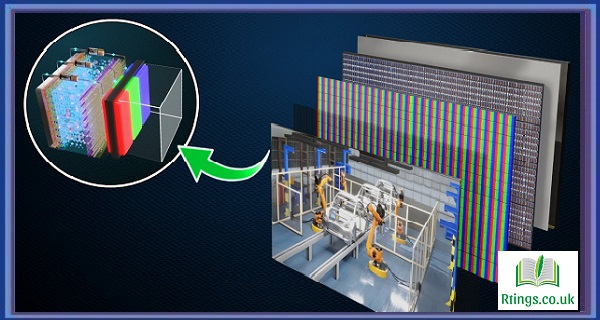
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology is the latest display technology used in modern TV sets. OLED technology produces deep blacks, high contrast, and vivid colors. The technology is based on the use of organic materials that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This guide will explain in detail how OLED technology works and how it differs from other display technologies.
What is OLED?
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. An OLED is made up of thin layers of organic materials sandwiched between two electrodes. When an electric current is applied to the electrodes, the organic materials emit light. Unlike traditional LCD or LED displays, OLED displays do not require backlighting, as each pixel is self-illuminating.
How does OLED technology work?
OLED technology works by utilizing organic materials that emit light when an electric current is applied to them. In an OLED display, each pixel is made up of an organic material that is placed between two electrodes. The electrodes are made up of a transparent conductive material like Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). When an electric current is applied to the electrodes, the organic material emits light.
There are two types of OLED displays, passive-matrix OLED (PMOLED) and active-matrix OLED (AMOLED). PMOLED displays use a simple matrix of OLEDs to form the display. They are cheaper to produce but need more size and resolution. On the other hand, AMOLED displays use a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane to control the current flow to each pixel. This allows for more extensive and higher-resolution displays.
In an AMOLED display, each pixel is controlled by a thin-film transistor that acts as a switch, turning each pixel on and off. When a pixel is turned off, it does not emit light, resulting in deep blacks. When a pixel is turned on, it emits light, producing bright colors. The amount of current applied to each pixel determines its brightness, allowing for precise control over the display’s luminance.
What are the advantages of OLED technology?
OLED technology offers several advantages over traditional display technologies like LCD and LED. Here are some of the key advantages of OLED technology:
- Deep Blacks: OLED displays are known for their ability to produce deep blacks, as each pixel can be turned off individually. This produces a high contrast ratio, making the display more vibrant and lifelike.
- Wide Viewing Angles: OLED displays have wider viewing angles than LCDs, making them more suitable for group viewing.
- Fast Response Time: OLED displays have a faster response time than LCDs, resulting in less motion blur and a smoother viewing experience.
- Thin and Lightweight: OLED displays are thinner and lighter than LCDs, making them easier to mount on walls or move around.
- Energy Efficient: OLED displays are more energy-efficient than LCDs, as they do not require backlighting. This can lead to lower electricity bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
What are the disadvantages of OLED technology?
While OLED technology offers several advantages, it also has some drawbacks. Here are some of the key disadvantages of OLED technology:
- Burn-in: OLED displays can suffer from burn-in, where static images can permanently damage the display over time.
- Limited Lifespan: OLED displays have a limited lifespan compared to LCDs. This is because the organic materials used in OLED displays degrade over time, decreasing brightness and color accuracy.
- Expensive: OLED displays are more expensive to produce than LCDs, making them more expensive.
- Color Shift: OLED displays can suffer from color shift, affecting color accuracy when viewed in off-angles.
Conclusion
OLED TV technology is a groundbreaking advancement in display technology that offers many benefits over other displays. It uses organic materials that emit light when an electric current is applied, allowing each pixel to be self-illuminating and providing a high contrast ratio and vibrant colors. While OLED displays can suffer from burn-in and have a limited lifespan, modern OLED displays have features like pixel shift and automatic brightness limiters to prevent burn-in and extend their lifespan. OLED technology is constantly evolving, and we can expect to see even more improvements in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes OLED technology different from other display technologies?
OLED technology differs from other display technologies like LCD and LED because it does not require backlighting. In an OLED display, each pixel is self-illuminating, which allows for deeper blacks, higher contrast, and wider viewing angles. OLED displays are more energy-efficient and have a faster response time than LCDs.
How do OLED displays produce deep blacks?
OLED displays can produce deep blacks because each pixel can be turned off individually. This is because OLED displays do not require backlighting, so when a pixel is turned off, it emits no light. This results in a high contrast ratio, making the display more vibrant and lifelike.
Can OLED displays suffer from burn-in?
Yes, OLED displays can suffer burn-in when static images can permanently damage the display over time. This is because the organic materials used in OLED displays degrade over time, decreasing brightness and color accuracy. However, modern OLED displays have pixel shifts and automatic brightness limiters to prevent burn-in.
How long do OLED displays last?
OLED displays have a limited lifespan compared to LCDs. This is because the organic materials used in OLED displays degrade over time, decreasing brightness and color accuracy. The lifespan of an OLED display can vary depending on usage, but it is generally estimated to be around 100,000 hours or 8-10 years of normal use. However, OLED displays have features like an automatic brightness limiter to extend their lifespan.